Nanostructures CeO2 for Sensing and Energy Device Applications
Sep 16, 2025
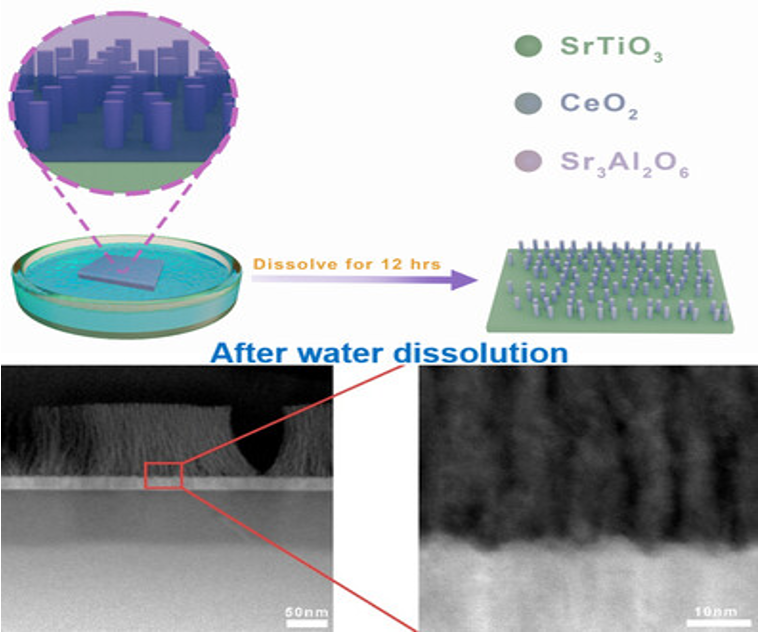
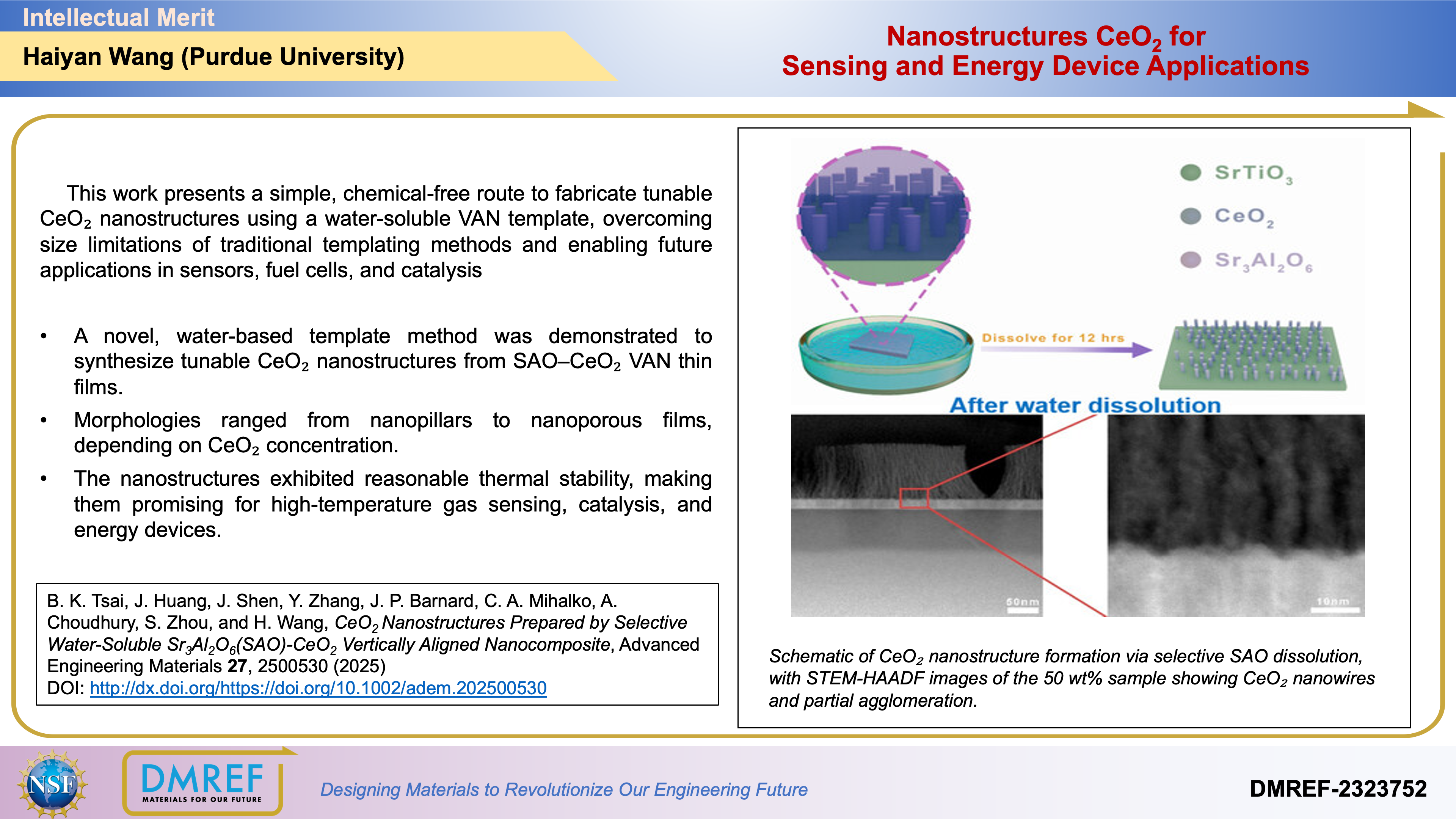
This work presents a simple, chemical-free route to fabricate tunable CeO₂ nanostructures using a water-soluble VAN template, overcoming size limitations of traditional templating methods and enabling future applications in sensors, fuel cells, and catalysis
A novel, water-based template method was demonstrated to synthesize tunable CeO₂ nanostructures from SAO–CeO₂ VAN thin films.
Morphologies ranged from nanopillars to nanoporous films, depending on CeO₂ concentration.
The nanostructures exhibited reasonable thermal stability, making them promising for high-temperature gas sensing, catalysis, and energy devices.