The Hidden Hierarchical Nature of Soft Particulate Gels
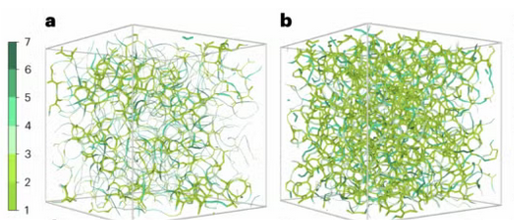
Soft particulate gels include materials we can eat, squeeze or 3D print, from foods to bio-inks to cement hydrates. They are composed of a small amount of particulate matter dispersed in a continuous fluid phase. The solid components assemble to form a porous matrix, providing rigidity and control of the mechanical response, despite being the minority constituent. The rheological response and gel elasticity are direct functions of the particle volume fraction. However, the diverse range of different functional dependencies reported experimentally has challenged efforts to identify general scaling laws. Here a hidden hierarchical organization of fractal elements is revealed that controls the viscoelastic spectrum, and which is associated with the spatial heterogeneity of the solid matrix topology. The fractal elements form the foundations of a viscoelastic master curve, constructed using large-scale three-dimensional (3D) microscopic simulations of model gels, which can be described by a recursive rheological ladder model over a range of particle volume fractions and gelation rates. The hierarchy of the fractal elements provides the missing general framework required to predict the gel elasticity and the linear viscoelastic response of these complex materials.